Beyond GeoLearning (Contextual mobile Learning)
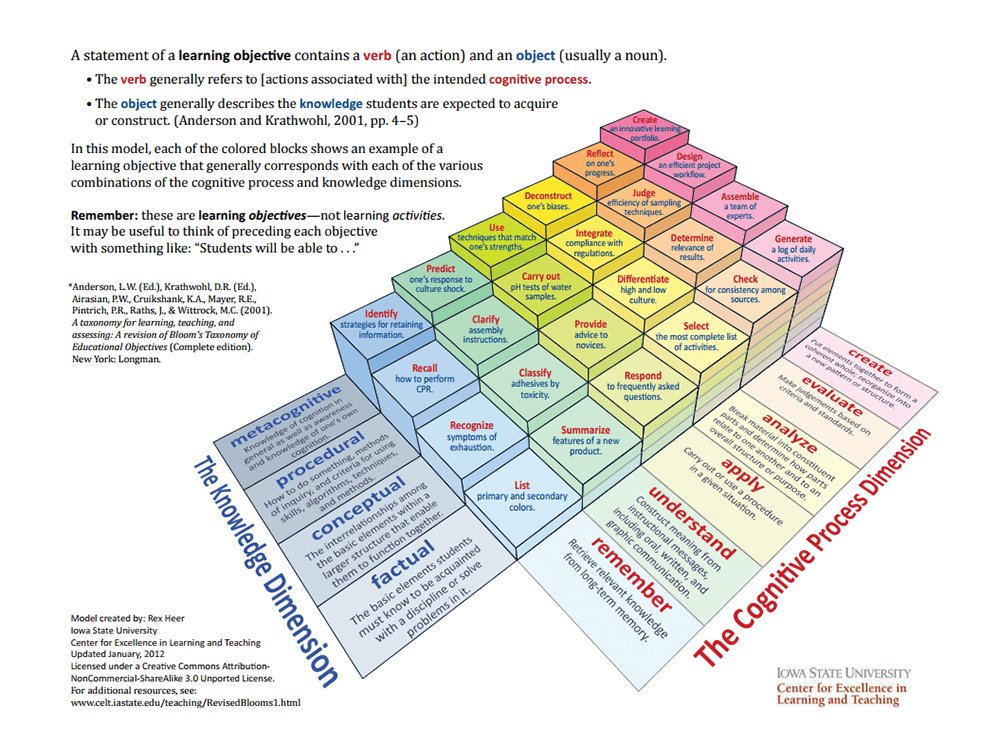
A 3 Dimensional Model Of Bloom’s Taxonomy by IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY
Definition
A didactic method (Greek: διδάσκειν didáskein, "to teach") is a teaching method that follows a consistent scientific approach or educational style to engage the student’s mind. - Theory of teaching (Wikipedia, 2014)
Didactic Platforms
List of important Edu-Pages based on geolearning:
- Educational Technology and Mobile Learning
- Top Learning Management System Software Products
- Edutech Wiki of University of Geneva
- UW-Stout Mobile Learning
Edu-Tools
List of Social Media and Social Networking tools for Education
- Moodle
- Google Drive / Google Docs
- TeamUp
- ClassDojo
- Padlet
- Edmodo
- Wordpress
- Prezi
- Youtube
- Blogger (Xanga)
- Wikis, WikiMe
- Augmented Reality Best Practise and Collection of Apps. Compare Map of AR SDKs
(Poll at ReserachGate, Dec. 2014)
AR creation apps, tools, and development platforms
Using Augmented Reality for Contextual Mobile Learning ( Jason Haag Nov.25, 2013)
Augmented Reality Brings New Dimensions to Learning (Todd Nesloney Nov. 4, 2013)
- ARIS (http://arisgames.org)
- Aurasma (http://aurasma.com)
- Junaio (http://junaio.com)
- Layar (http://layar.com)
- Metaio (http://metaio.com)
- Vuforia (http://vuforia.com)
- Wikitude (http://wikitude.com)
Learning Managment Systems
Typical features are a Learning Managament Systems defines are listed here:
- Course Management, e.g. lists of courses, registration, credit information and syllabus, pre-requisites
- Teaching Materials, i.e. courseware
- Self-assessment quizzes
- Lessons tools: Authoring for contents (structured XML or HTML) and quizzing/testing (e.g. Java Script generators) or alternatively ability to import standard IMS orSCORM packages developed with an external tool (e.g. Dreamweaver).
- Asynchronous Communication: email, forums
- Synchronous Communication: chat, whiteboard, teleconferencing,
- Student tools: Home page, self tests, bookmarks, progress tracking, ....
- Student Management Tools: progress tracking, on-line grading (assessment), ....
- Learner feedback: course evaluation surveys, test evaluation surveys etc.
Mobile Learning Design Solutions
The potential for multi-functional and individualized learning through mLearning applications pushes the boundaries of traditional educational tools, which were typically confined by content, location and functionality. It is therefore of critical importance to define new ways for understanding how learning occurs with mobile technologies and to improve methods for analysing learning outcomes. This requires a careful examination of the various aspects of an mLearning initiative that influences how, where and why applications are used, as well as an understanding of the human interactions that occur during and after use and the changes in human behaviour and learning that result. (Murphy et al. 2014)
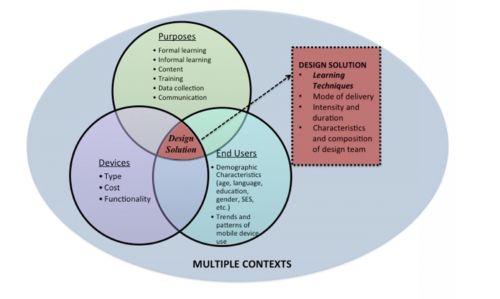
Figure 1: Design solution components (Murphy et al. 2014)
A huge link collection aboutz mobile Learning with Cell Phones is available at Cybrary Man's website.
References
Murphy, Katie M., et al. "Mobile Learning Design Solutions." Methodological Challenges When Exploring Digital Learning Spaces in Education. SensePublishers, 2014. 13-27.
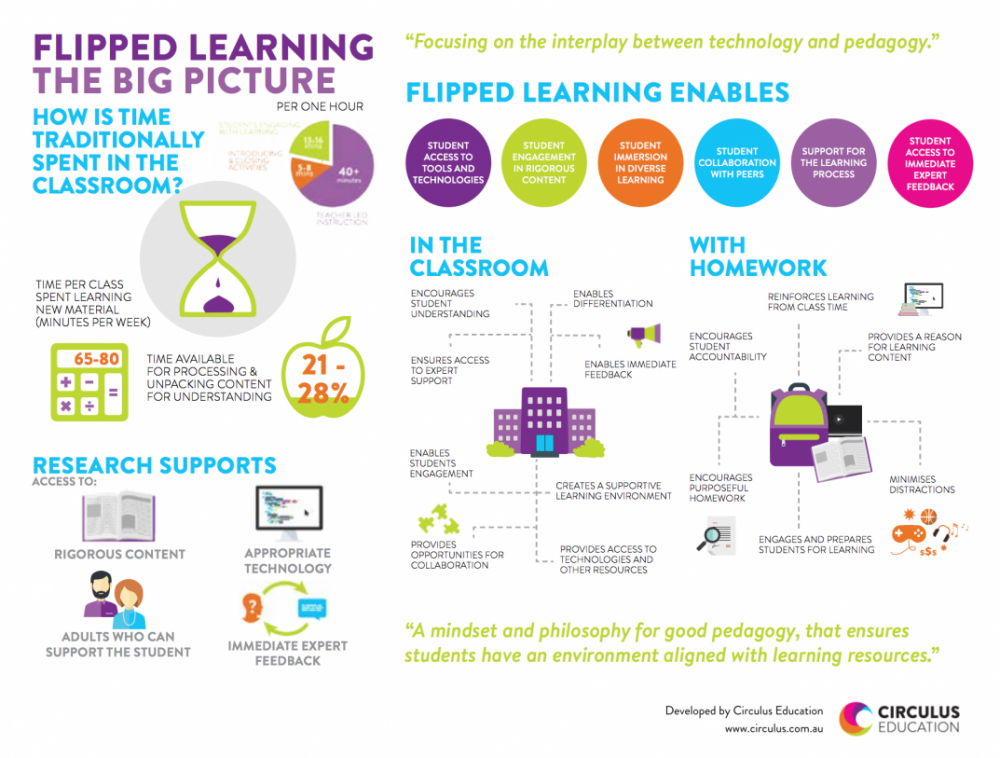
Flipped learning
[http://circulus.com.au/flipping-for-successful-learning, 2015]
Education 3.0
We have been educated in a 1.0 education model, we are teaching in a 2.0 model but our students are living in a 3.0 model. These three models chronicle the major paradigmatic shifts that education has witnessed over the last century. They also represent, in an ironical way, the huge abyss between the actual needs of our students and what is actually being delivered to them in schools.
Below is a very interesting chart created by Dr John Moravec in which he compares between the three models we mentioned above. Have a look and share with us what you think of it. Enjoy.
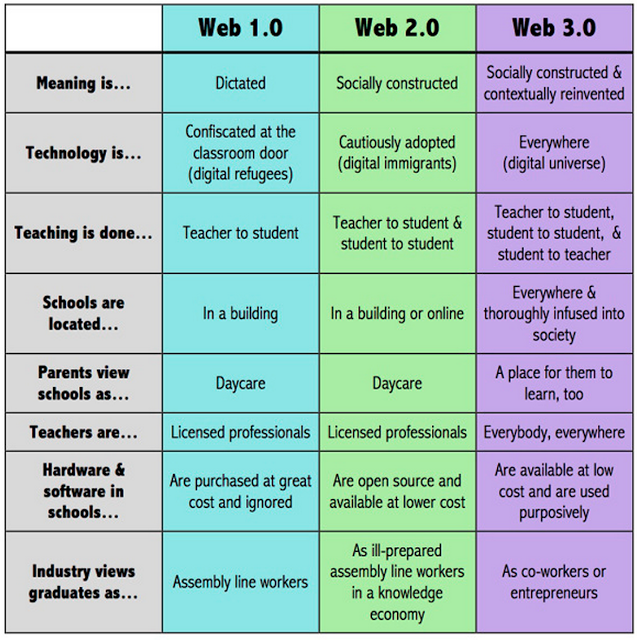
Edu Blogpost
Das Ende der Didaktik - Wie Smartphones schulisches Lernen revolutionieren // Vortrag Didacta Philippe Wampfler
October 2014, Didacta/Worlddidac Basel
Mobile Learning Theorie und Praxis
April 2012, Switch SIG Mobile Learning Meeting